Montelukast: Reminder of the risk of neuropsychiatric reactions and measures for its safe and effective use.
Montelukast is a leukotriene receptor antagonist that reduces inflammation and prevents asthma attacks. It is used to prevent wheezing, difficulty breathing, chest tightness, and coughing caused by asthma in adults and children 12 months of age and older. Montelukast is also used to prevent bronchospasm (breathing difficulties) during exercise in adults and children 6 years of age and older.
Montelukast is an active pharmaceutical ingredient which is available in multiple brands like Singulair, Montair, Odimont, Montek, Telekast, Montemac, Lukotas, Lasma, Montevac etc.
This update is to remind and strengthen awareness for safe and effective use of Montelukast.
Product labels of montelukast were updated with neuropsychiatric adverse reactions [listed below] in the year 2019.
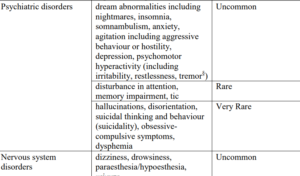
Neuropsychiatric side effects of Montelukast
MHRA continued to received case reports relevant to these adverse reactions associated with montelukast use since the label update.
Despite the presence of safety warnings in labels, MHRA has identified that there is potential lack of awareness of the risk of neuropsychiatric reactions with montelukast amongst healthcare professionals, patients and their caregivers.
Based on the overall safety evidence, Pharmacovigilance Expert Advisory Group (PEAG) advised that montelukast should be immediately withdrawn due to the nature of the neuropsychiatric reactions, and that immediate withdrawal may help prevent escalation to more serious events.
Boxed Warning: To increase awareness of these neuropsychiatric effects montelukast, new boxed warnings are being introduced to the Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC) and Patient Information Leaflet (PIL) to make these risks more prominent to the reader. The warnings in these labels for all montelukast products in the UK have been strengthened and highlighted with a black box for greater emphasis.
Important note for healthcare professionals:
- It is well established that neuropsychiatric reactions may occur uncommonly [1 in 1000 patients] in association with montelukast. Therefore, safety information in product labels updated to ensure that patients and healthcare professionals are aware of these risks and what action should be taken for safe and effective use of this medicine.
- Be aware of neuropsychiatric adverse reactions associated with Montelukast.
- Advise patients and their caregivers to aware of the list of these reactions and to seek medical attention immediately should they occur.
- Assess the therapeutic benefit and discontinue montelukast if patients experience new or worsening symptoms of neuropsychiatric reactions.
- Report all suspected adverse drug reactions associated with montelukast to the your national ADR reporting centre.
Important note for Public (Patients/patient care providers):
Before using montelukast:
- Be aware of boxed warnings for this product.
- Discuss with your healthcare provider abut all your relevant medical history other concurrent conditions or medications being used.
After using montelukast:
- Observe if you identify any signs or symptoms of these adverse reactions in you or for your patient (if you are a care provider), then immediately report your experience to your doctor.
- Do not discontinue montelukast without consulting your doctor or pharmacist.
Voluntary ADR reporting:
Every medicinal product has both benefits and risks. Medicines are authorized to market based on the favourable benefit-risk profile anticipated at the time of regulatory approval/entry into market. However, the safety profile of medicine would continuously updates owing to safety data from the post marketing experience from public. If the rate of reporting of suspected adverse drug reactions (ADR) from public is line with the actual occurrence of ADRs, the time lapse for taking regulatory action can be reduced and thereby improving patient safety.
All health care professionals and consumers of pharmaceutical medicinal products are encouraged to be aware of this fact and observe/monitor for any possible adverse events, reactions, medication errors, or quality complaints of medicinal products and report the same to your respective national health authority.
This would accumulate safety evidence for medicinal products which in turn help health authorities to take regulatory actions at the earliest possibility for a better patient safety and overall public health.